Laser Diodes
Laser Diodes Greatly Changed Optical Sensing and Material Processing
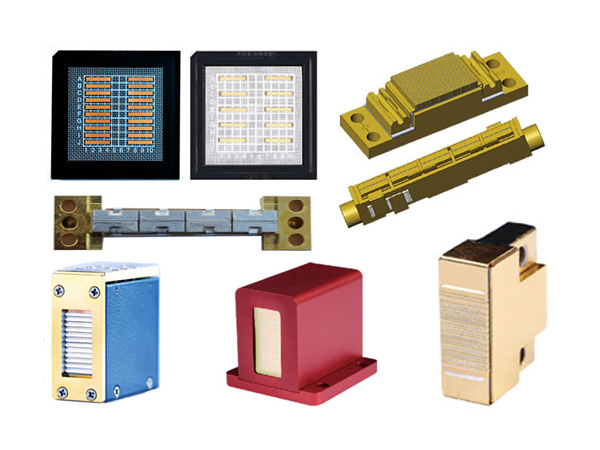
Laser diodes are a type of laser generator whose working materials are semiconductors and belongs to solid-state lasers. Most laser diodes are structurally similar to general diodes. Due to the fact that the energy transformation process of electrons in laser diodes during operation only involves two energy levels and does not result in energy loss caused by indirect bandgap, the efficiency is relatively high. In addition to high efficiency, laser diodes also have the advantages of small size and long lifespan, with a unit price of less than US$1 for mass-produced ones.
At present, the main types of laser diodes are single heterostructure (SH), double heterostructure (DH), and quantum well (QW). Products on the market can provide various wavelengths from ultraviolet to long wavelength infrared light. The central wavelength is determined by the device structure and semiconductor material. The following figure shows the main application areas of laser diodes.
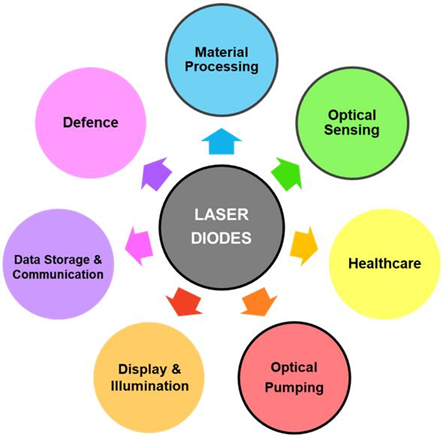
The power output range provided by a single laser emitter can range from milliwatts to several watts. Each laser emitter can be used alone or combined into a laser diode strip for solid-state laser pumping, or integrated into a laser diode module to meet various application requirements. Over the past thirty years, the average power of laser diodes has increased exponentially, while their average price has decreased exponentially. Semiconductor laser technology has made incredible progress, enabling the development of sub-kilowatt direct diode lasers (DDL) and several kilowatt high-power direct diode lasers (HPDDL). The significant improvement in beam quality has made DDL an important tool for metal processing. DDL and HPDDL are becoming the main development trends in the global industrial manufacturing field. The recent innovation is mainly the development of blue light diode lasers for welding and 3D printing of copper materials.
 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch euskara
euskara Русский язык
Русский язык Italiano
Italiano Português
Português Nederlands
Nederlands Polski
Polski Greek
Greek Lietuva
Lietuva Türkçe
Türkçe 日本語
日本語 한어
한어 中文
中文 தாமில்
தாமில் فارسی
فارسی हिंदी
हिंदी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Pilipino
Pilipino Indonesia
Indonesia தாமில்
தாமில்